1. What is a shielded wire?
Definition: The conductor wrapped around the conductor is called the shielding wire, and the wrapped conductor is called the shielding layer, which is generally a braided copper network or copper berth (aluminum). The shielding layer needs to be grounded, so that external interference signals can be imported into the earth by this layer.
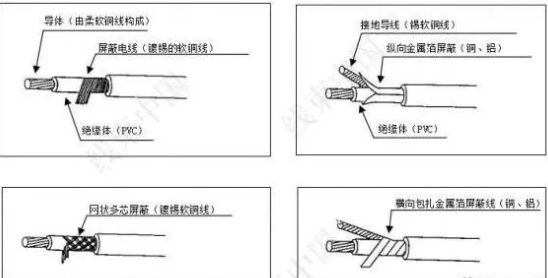
The shielding layer of the shielded cable is mainly made of copper, aluminum and other non-magnetic materials, which is very thin. The effect of the shielding layer is not mainly due to the reflection and absorption of the electric field and magnetic field by the metal body itself, but due to the grounding of the shielding layer. The different forms of grounding will directly affect the shielding effect. Grounding methods for electric field and magnetic field shields are different. It can be ungrounded, single-ended grounded, or double-ended grounded.
The role of the shielding wire: to avoid interference signal into the inner layer, conductor interference and reduce the loss of the transmitted signal.
The shielding wire isolates the electromagnetic noise source from the sensitive equipment and cuts off the transmission path of the noise source. Shielding is divided into active shielding and passive shielding. The purpose of active shielding is to prevent the noise source from radiating outward. It is the shielding of noise source. The purpose of passive shielding is to prevent the sensitive equipment from being interfered with by noise sources. It is the shielding of sensitive equipment.
Structure: (ordinary) insulation layer + shielding layer + wire; (Advanced) insulation layer + shielding layer + signal conductor + shielding grounding conductor
Note: When selecting the shielding wire, the insulating layer of the shielding ground wire has the conductive function and can be conductive with the shielding layer (with a certain resistance).
2. Principle of shielded cables
Shielding wiring system originated in Europe, it is outside of the common unshielded cabling system plus metal shielding layer, using metal shielding layer of reflection, absorption and skin effect, we can realize the function of preventing electromagnetic interference and electromagnetic radiation, shielding system balance principle of comprehensive utilization of the twisted pair and shielding layer shielding effect, thus has very good characteristics of electromagnetic compatibility (EMC).

Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) refers to the ability of electronic devices or network systems to resist electromagnetic interference without generating excessive electromagnetic radiation. In other words, it is required that the equipment or network system can work normally in a relatively harsh electromagnetic environment, and at the same time can not radiate excessive electromagnetic waves to interfere with the normal work of other equipment and network around.
The balance characteristics of U/UTP(unshielded) cables do not depend solely on the quality of the component itself (e.g., the pair), but can be affected by the surrounding environment. This is because metal around the U/UTP (unshielded), hidden "ground," pulling during construction, bending, and so on can destroy its balance characteristics and thus degrade EMC performance.
Therefore, there is only one solution to achieve a durable balance: ground all the wires with an extra layer of aluminum foil. Aluminum foil adds protection to the fragile twisted-pair wires and creates an artificially balanced environment for U/UTP (unshielded) cables. This formed what we now call a shielded cable.
Shielded cable shielding principle is different from the offset balance principle of twisted-pair, shielded cable is outside of the four pairs of twisted-pair add one more layer or two layers of aluminum foil, using metal to the electromagnetic wave reflection, absorption and skin effect principle, effective to prevent external electromagnetic interference into the cable, but also to prevent internal radiation signal, interference of other equipment work.
Note: Skin effect means that the distribution of current on the conductor section tends to be on the conductor surface with the increase of frequency. The higher the frequency, the smaller the skin depth, that is, the higher the frequency, the weaker the penetration ability of electromagnetic wave.
The experimental results show that the electromagnetic wave with frequency over 5MHz can only pass through the 38μm thick aluminum foil. If the thickness of the shield is allowed to exceed 38μm, the frequency of electromagnetic interference that can enter the cable through the shield is mainly under 5MHz. For the low frequency interference below 5MHz, the balance principle of twisted-pair can be used to cancel the interference effectively.
According to the earliest definition of cabling, there are two types of cabling: unshielded cable-UTP and shielded cable-STP. Later, with the development of technology and different processes, many different types of shielding have been derived
1. F/UTP Foil Screened Cable monolayer aluminum foil screened structure
2.2. Foil and Braid Screened Cable double-layer shield structure in copper braided mesh
a)SF/UTP aluminum foil and braided copper mesh are simultaneously wrapped around the outer layer of the four pairs of wires
b) S/FTP (PIMF) wire Pair single pair aluminum Foil shield plus copper braided mesh wrapped in the outer layer of four pairs of wire PIMF =Pair in Metal Foil.
The shielding cable resists external interference mainly in the following aspects: the integrity of signal transmission can be guaranteed by the shielding system. The shielded wiring system can protect the transmitted data from external electromagnetic interference and RF interference. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) basically is low frequency interference, motor, fluorescent lamp and power cord are the usual electromagnetic interference source. Radio frequency interference (RFI) is high-frequency interference, mainly wireless frequency interference, including radio, television relay, radar and other wireless communications.
For resistance to electromagnetic interference, the braided shield, the metal mesh shield, is the most effective because of its low critical resistance. For RF interference, foil shielding is the most effective, because the gaps created by the metal mesh shielding allow high-frequency signals to flow in and out freely. For the mixed interference field of high and low frequency, the combined shielding method of metal foil layer and metal mesh should be adopted, that is, the double-layer shielded cable in the form of S/FTP. In this way, the metal mesh shielding is suitable for the interference in the low frequency range, and the metal foil shielding is suitable for the interference in the high frequency range.
The thickness of the aluminum foil shield layer in the shielded cable of IBM ACS is 50-62μm, which provides a more complete shielding effect. At the same time, because only a single shield is used, it will be more simple for the construction, easy to install, not easy to cause artificial damage in the construction process, and the thickness of aluminum and silk can withstand greater destructive power. Thus can provide users with higher quality transmission performance.
3.Shielded wire connection
One end of the shielded wire is grounded and the other end is suspended.
When the signal transmission distance is far, due to the different grounding resistance or PEN at the ends of the line current, may lead to two different ground potential, as if on both ends of grounding, shielding layer there is electricity pop into, instead of to form interference signal, so this kind of circumstance commonly adopt grounded at one end, the other end dangling, can avoid this kind of interference.
Both ends of the grounding shielding effect is better, but the signal distortion will increase.
Please note: the two layers of shielding should be mutual insulation isolation type shielding! If there is no insulation from each other should still be regarded as a single shield!
The outermost shielding ends of the ground is due to the introduction of the potential difference and induced current, so the magnetic flux to reduce the strength of the source magnetic field, which basically cancels out the voltage induced when there is no outer shielding layer;
The innermost shielding end is grounded, because there is no potential difference, only for general anti-static induction.
The principle is:
1. One end of the single shield is grounded, no potential difference is formed, generally used for anti-static induction.
2. Double layer shielding, the outermost shield is grounded at both ends, and the inner shield is grounded at equal potential. At this point,the outer shield induces a current due to the potential difference,thus generating a flux that reduces the strength of the source magnetic field and thus essentially canclels out the voltage induced in the absence of the outer shield.
To prevent electrostatic interference, a single point of grounding is required, whether it is a layer 1 or layer 2 shield. Because a single point grounding is the fastest electrostatic discharge.
Except, however, in the following two cases:
1,external strong current interference, single point grounding can not meet the fastest discharge of static electricity.
If the cross-sectional area of the grounding cable is large enough to ensure the fastest electrostatic discharge, the grounding cable must also be single. Must be two layers of shielding, the outer shielding is mainly to reduce the intensity of interference, not to eliminate the interference, then must be multipoint grounding, although not finished, but must be weakened as soon as possible, to weaken, multipoint grounding is the best choice.
For example, the cable tray in the enterprise is actually the outer shielding layer, which must be multipoint grounded, the first line of defense, to reduce the intensity of interference sources.
The inner shield layer must be single point ground, because the external strength has been reduced, as soon as possible discharge, eliminate interference is the purpose of the inner layer.
2, external electric shock and lightning protection and other safety requirements.
In this case, two layers of protection are required. The outer layer is not used to eliminate interference. The outer layer is used to ensure the safety of people and equipment. The inner layer is what prevents interference, so it must be grounded in a single point.
4.Conclusion:
Single end grounding:
1) The single-end grounding of the shielded cable is helpful to avoid the interference of low-frequency electric field. Or it can avoid frequency interference with wavelength λ much larger than the cable length L.
2) Single-terminal grounding of the cable shield layer can avoid the low-frequency current noise on the shield layer. This current internally causes a common-mode interference voltage and has the potential to interfere with analog devices.
3) Single terminal grounding of the shield is desirable for circuits that are sensitive to low frequency interference (analog circuits).
4) Fluctuation and permanent deviation of continuous measurement value indicate low-frequency interference.
Double terminal grounding:
1) Ensure that the connection to the electric control cabinet or plug (circular contact) passes through a large conductive area (low induction coefficient). It is better to choose metal on metal than non-metal on non-metal.
2) Since some analog modules use pulse technology (for example, the processor and A/D converter are integrated in the same module), it is recommended that analog signals be shielded from each other to ensure correct equipotential connection, and only in this case, double terminal grounding.
3) Usually, the transmission impedance of the metal foil shielding layer is much larger than that of the copper braided wire, and its effect is 5-10 times different, so it cannot be used as a digital signal cable.
4) Occasional malfunction indicates high-frequency interference. This is not eliminated by equipotential connections of wires.
5) In addition to the end of the cable, it is advantageous to ground the shielding layer at multiple points.
6) Do not connect the shielding layer to the pin to avoid the "pig tail" phenomenon.
7) Always pay attention to the parallel impedance of the shield layer should be less than 1/10 of its own impedance. Cable tray, mechanical frame, other shielding layers or other parallel cables can make the system equal potential.
8) If the cable shield layer is hot when the shield layer is grounded at both ends, or the shield layer sparks when it touches the shell of the electric control cabinet or the shield bus, the equipotential connection is not reliable.
For more informations,Contact us!
Email: sales03@aichie.com
Whatsapp/Mobile/Wechat: (86) 18027502150