Nowadays, with the continuous emergence of new services such as cloud computing, big data, and 5G, the scale of data centers continues to expand, and its architecture and wiring are becoming more and more complex, while the lightweight and gradually reduced cost of optical fiber make the demand for optical fiber in the backbone network equipment more and more vigorous, and the proportion of optical fiber in large data centers is higher than 70%, far higher than copper cable. Many twisted pair practitioners are worried that the copper cable will be completely replaced by optical fiber. Having recently reviewed the regulations and done a brief market demand survey, Based on the latest international standard ISO1181:2017 and ANSI/TIA-TIA-568.2-D as the main body of the data center wiring application technology evolution, international standard update content refining, as well as the future of the data center application direction for China's future data center application data sorting found, Cat.8 40G can fill the gap of copper twisted pair in 40G transmission applications.

Although, driven by the demand for higher bandwidth in the data center, optical fiber with higher transmission rate, larger bandwidth and other advantages make its deployment in the data center occupy a large share, especially the backbone application network; But in fact, copper cable will still be an indispensable part of the data center, and in the application of voice transmission, power supply and other special environment and in the transmission of voice signals and wireless access, POE power supply system and other power supply applications, optical fiber can not replace copper cable.
First, because copper cable and optical fiber is different from the transmission of data through electrical pulses, can support voice signals, therefore, copper cable can be applied to voice transmission, and optical fiber can not.
Second, because the glass fiber used in the optical fiber cannot conduct electricity, the copper in the copper cable can conduct electricity
Therefore, copper cable can supply power at the same time of data connection, which is widely used in wireless access, POE power supply system, LED-based power system, etc. Copper cable is the cable that can not be replaced by optical fiber, TIA standard - TIA 568.2-D describes in detail the application scenario that is not indispensable:
1. The copper cable section mentions the relevant content and application requirements of 25GBase-T and 40GBase-T based on Cat8 level.
2. The double coaxial balanced cable DAC part is supplemented with 100GBase-CR2, 100GBase-CR4 and 200GBase-CR4.
3. Data center backbone fiber technology increased by 200G/400G based on IEEE802.3bs and IEEE802.3cm applications of a variety of fiber transceiver types, application distance and other definitions, this time introduced the latest OM5 fiber technology.
4. The latest IEEE802.3bt POE standard is introduced, which will be used in the data center building in various intelligent systems.
5. Defined the requirements for the highest attenuation value of each single mode and each multi-mode fiber from 1GB-64GB applications based on FCIA in SAN networks.
6. The chapter on Design Principles focuses on the different redundant connection models defined by international standards under the network scale of EOR and TOR under different architectures.
7. Added the analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of various network architectures such as tree, leaf ridge, whole network and so on.
8. Recommended the application scenarios of the network and cabling architecture of different data center types such as enterprise data center, IDC, micro module, EDGE and other four types of data center.

In addition, the modular plug termination link (MPTL) as an option to connect devices in the TIA-568.2-D standard will promote the growth of RJ45 copper cable applications, especially in surveillance systems using IP cameras. At the same time, the appendix to this specification also adds 28AWG specification network jumpers, and smaller specifications of copper cables will help air circulation and space utilization, so that it can be developed in high-density applications.
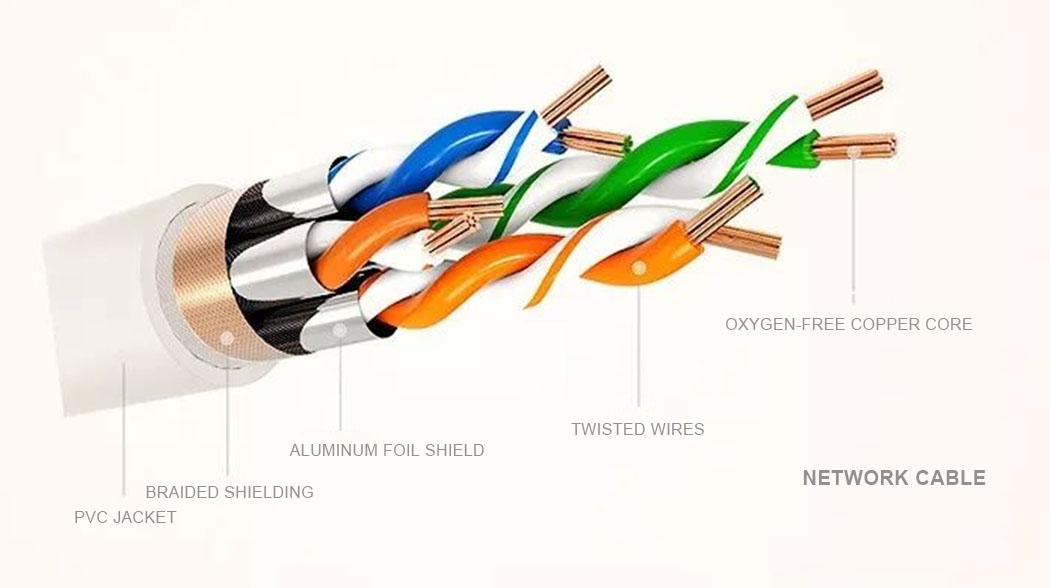
There are many types of copper cables on the market today, such as Cat5, Cat6, Cat7 and Cat8 network jumpers, and different types of copper cables have different wiring applications.
Here are the differences:
1. Super Category 5 network jumpers
Category 5 network jumpers (that is, Cat5e network cable) is developed by TIA/EIA in 2001, with small attenuation, less crosser, maximum bandwidth of 100MHz, maximum transmission rate of 1000Mb/s, backward compatible, relative to the category 5 network cable, its performance has been greatly improved. It has a higher attenuation crosstalk ratio (ACR) and channel noise ratio (SNR), and a smaller delay error. Super Category 5 network jumpers are suitable for 100 and gigabit Ethernet and are commonly found in home networks or indoor cabling.
2. Category 6 network jumpers
Category 6 network jumpers (Cat6 network cables) have a bandwidth of 250MHz and a maximum transmission rate of 10Gb/s. Compared with super Category 5 network jumpers, the internal structure of the Category 6 network jumpers is better, in which the internal cross skeleton is used, and the twisted pair of four pairs is smaller, so that the performance of the Category 6 network jumpers is improved in terms of crosstalk and return loss, and the transmission performance is much higher than that of the super Category 5 network jumpers, and it is more suitable for applications with transmission rates greater than 1Gbps. In addition, under normal circumstances, the maximum transmission distance of Category 6 network jumpers does not exceed 55 meters.
3. Super Category 6 network jumpers
Super Category 6 network jumper (Cat6a network cable) is an improved version of Category 6 network jumper, its bandwidth is twice that of Category 6 network jumper, the transmission frequency can reach 500MHz, and the maximum transmission rate is 10Gb/s. Due to the excellent structure of the Super Category 6 network jumper, it helps to eliminate external crosstalk (AXT), so it can support distances up to 100 meters. In addition, compared with Category 6 network jumpers, the conductor material of super Category 6 network jumpers is thick and more suitable for industrial environments.
4. Category 7 network jumpers
Category 7 network jumpers (Cat7 network cable) transmission frequency of up to 600 MHz, in the transmission distance of 100 meters to support 10Gbps transmission rate, suitable for 10 Gigabit Ethernet. Compared with previous generations of network jumpers, the Category 7 network jumpers have strong shielding, can effectively reduce attenuation, and are suitable for the connection of switches, distribution frames and other equipment in high-density data centers. It is worth mentioning that the transmission rate of Category 7 network jumpers can be as high as 40Gbps at a transmission distance of 50 meters, and even up to 100Gbps at a transmission distance of 15 meters. At present, because the Category 7 network jumpers are not flexible and easy to manage, they have not been popularized for the time being.
5. Category 8 network jumpers
Category 8 network jumpers(Cat8 network cable)was ratified by the TR43 working group under ANSI/TIA 568-C.2-1. It is defined up 2000 MHz and only for distances from 30 to 36m depending on the patch cords used. ISO is expected to ratify the equivalent in 2018 but will have 2 options:
Class I channel (Category 8.1 cable): minimum cable design U/FTP or F/UTP, fully backward compatible and interoperable with Class EA (Category 6A) using 8P8C connectors
Class II channel (Category 8.2 cable): F/FTP or S/FTP minimum, interoperable with Class FA (Category 7A) using TERA or GG45 connectors.
Category 8 is designed only for data centers where distances between switches and servers are short. It is not intended for general office cabling.
There is no doubt that copper cable still occupies an important position in voice transmission, indoor network, horizontal wiring, POE system and other aptplicaions, and will not be completely replaced by optical fiber, and copper technology is still under continuous research and development, especially the popularization and application of CAT8 and CAT9, which can meet the needs of more equipment connection in the future. Therefore, you do not need to worry that the copper cable will be obsolete by The Times.
Aichie Tech has always been in a leading position in the R&D and production of wire and cable. The company's cable products have obtained UL certification for many times, and have been widely recognized and used around the world. The company's wire and cable products include electronic wires, automotive wires, medical cables, industrial control cables, silicone wires, high-voltage cables, energy storage cables, new energy charging cables and other wires, which are widely used in automobiles, industries, construction, medical, subway, robot, motors Servo system and other fields.
If you have any needs about wire and cable, you can contact Dongguan Aichie Tech Electronics Co Ltd., we will provide high-quality wire and cable products to meet customer needs.E-mail: sales03@aichie.com